1. Introduction
The gas engineering industry plays a critical role in the global energy landscape, encompassing everything from natural gas extraction to distribution and utilization. Empowering and Transformative Gas Engineer Software: Revolutionizing the Industry for a Brighter 2024.As the demand for cleaner energy sources increases, gas engineers find themselves at the forefront of innovation and safety challenges.
The integration of technology, particularly software solutions, has become essential for enhancing efficiency and ensuring compliance with stringent safety standards. This article explores the various aspects of gas engineer software, highlighting its significance in transforming the industry.
2. Understanding Gas Engineering
Gas engineering involves the study and application of engineering principles related to the production, transportation, and utilization of gaseous fuels. Gas engineers work in diverse sectors, including oil and gas extraction, power generation, and residential services. Their responsibilities range from designing gas systems to ensuring compliance with safety regulations.

Despite the critical role they play, gas engineers face several challenges, including outdated methodologies, regulatory compliance, and the need for real-time data analysis. The adoption of advanced software solutions can help mitigate these challenges, providing engineers with the tools necessary to optimize their workflows.
3. The Role of Software in Gas Engineering
Specialized software plays a pivotal role in modern gas engineering practices. By automating routine tasks, providing real-time data analysis, and enhancing collaboration among teams, software solutions significantly improve operational efficiency. The benefits of using gas engineer software include:
- Streamlined Workflows: Automating routine tasks reduces manual errors and frees up engineers to focus on complex problem-solving.
- Enhanced Data Management: Centralized databases allow for better data organization and retrieval, crucial for compliance and reporting.
- Improved Collaboration: Cloud-based software enables real-time collaboration among teams, regardless of location.
Common types of software used in gas engineering include design software, maintenance management systems, and compliance tracking tools.
4. Key Features of Gas Engineer Software
Gas engineer software solutions come equipped with a range of features tailored to the unique needs of the industry:
- Design and Simulation Tools: These tools allow engineers to create and test gas system designs, optimizing performance and ensuring compliance with safety standards.
- Compliance and Regulatory Features: Integrated compliance modules help engineers track and adhere to local and international regulations, reducing the risk of penalties.
- Maintenance and Management Capabilities: Software solutions often include modules for scheduling maintenance, tracking inventory, and managing service requests, enhancing overall operational efficiency.
- Data Analytics and Reporting Tools: Advanced analytics capabilities enable engineers to derive insights from data, helping them make informed decisions and improve system performance.
5. Popular Gas Engineer Software Solutions
Several software platforms are gaining traction in the gas engineering sector, each offering unique features and functionalities.
- AutoCAD: Widely used for design and drafting, AutoCAD is a staple in many engineering disciplines, including gas engineering.
- PipeFlow: This software specializes in fluid flow calculations and offers tools for designing and analyzing gas distribution systems.
- SAP EAM (Enterprise Asset Management): Known for its robust asset management capabilities, SAP EAM helps gas engineers manage equipment, schedule maintenance, and ensure compliance.
- PSS SINCAL: A powerful simulation tool for analyzing the performance of gas networks, PSS SINCAL enables engineers to optimize system designs and operations.
Each of these platforms has case studies showcasing their successful implementation, resulting in enhanced efficiency and compliance.
6. Impact on Efficiency and Safety
The integration of software in gas engineering has profound implications for both efficiency and safety. By automating routine tasks and providing real-time data, engineers can quickly identify issues and address them before they escalate. For instance, predictive maintenance tools can forecast equipment failures, allowing teams to take preventive measures.
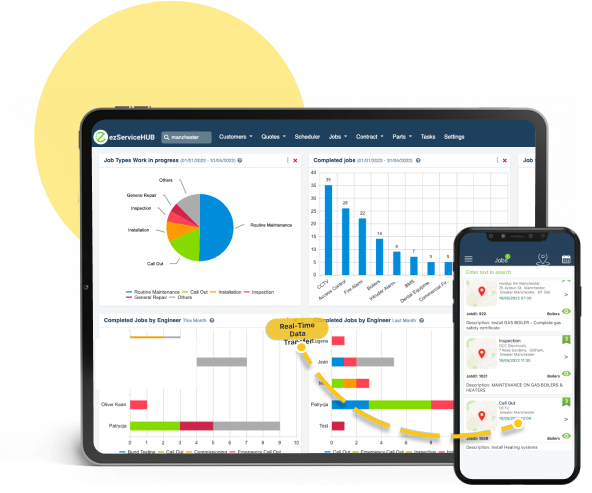
Moreover, software solutions enhance safety protocols by ensuring compliance with regulations and providing comprehensive documentation. In one notable case, a gas distribution company reported a 30% reduction in accidents after implementing a comprehensive software solution for compliance tracking and reporting.
7. Challenges in Implementing Software Solutions
While the benefits of gas engineer software are clear, the industry faces challenges in adoption. Common barriers include:
- Resistance to Change: Many engineers are accustomed to traditional methods and may resist transitioning to new software solutions.
- Integration Issues: Integrating new software with existing systems can be complex, leading to operational disruptions.
- Training and Education: Ensuring that all team members are adequately trained on new software is crucial for successful implementation.
To overcome these challenges, companies should focus on providing comprehensive training, engaging employees in the transition process, and ensuring robust technical support.
8. Future Trends in Gas Engineering Software
The future of gas engineering software is promising, with several emerging technologies set to revolutionize the industry:
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI-powered tools can analyze vast amounts of data to identify patterns and predict maintenance needs, further enhancing operational efficiency.
- Internet of Things (IoT): IoT devices can monitor gas systems in real time, providing valuable data for analysis and decision-making.
- Cloud Computing: The shift towards cloud-based solutions allows for greater flexibility and collaboration among engineering teams.
As these technologies continue to evolve, ongoing education and training will be essential for gas engineers to stay ahead of the curve and fully leverage the potential of software solutions.
9. Conclusion
In conclusion, gas engineer software is transforming the gas engineering industry by enhancing efficiency, improving safety, and enabling better compliance with regulations. As technology continues to advance, it is crucial for gas engineers and companies to embrace these solutions to remain competitive and address the challenges of the modern energy landscape. By investing in the right software and prioritizing ongoing training, the industry can look forward to a future of innovation and success

I am a Writer and Blogger at techsensc.com If you have any query or Question contact me at:
info.techsenc@gmail.com

